How AI is Transforming Diagnostics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the landscape of diagnostic medicine by introducing unprecedented precision, speed, and scalability. From radiology to pathology and genomics, AI algorithms are now integrated into systems that support or even outperform human diagnosticians in specific domains.
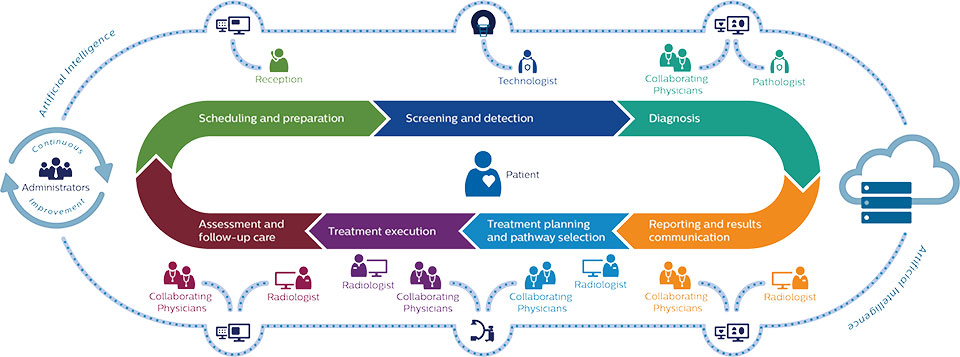
Radiology: A Flagship Use Case
AI-powered image analysis tools like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with remarkable accuracy. Studies have shown that deep learning models match or exceed radiologist performance in identifying conditions like pneumonia, breast cancer, and brain hemorrhages.
“AI acts as a second reader, reducing oversight and enhancing diagnostic confidence.” — Dr. Henry Lawson, Department of Radiology, Stanford
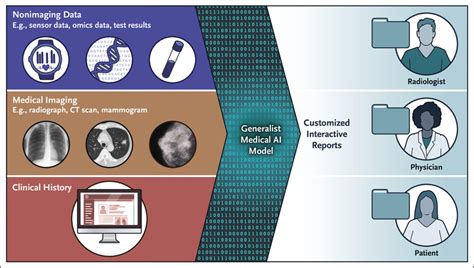
Pathology and Genomics
In digital pathology, AI assists in detecting rare cancer subtypes, quantifying tumor burden, and identifying cellular abnormalities that may escape human scrutiny. In genomics, machine learning accelerates the interpretation of variants of unknown significance in DNA sequences, aiding rare disease diagnostics and personalized medicine.
Benefits and Limitations
- Improved diagnostic speed and consistency
- Early detection of subtle patterns
- Resource efficiency in underserved regions
- Risk of algorithmic bias and overfitting
- Reliance on high-quality labeled data
Regulatory bodies like the FDA have already cleared dozens of AI-driven tools under the Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) framework. However, ongoing evaluation and transparent validation remain essential to safe integration into clinical workflows.
“We must balance innovation with oversight — algorithms should augment, not replace, human expertise.” — Prof. Anya Sobol, Biomedical Informatics, MIT← Back to Home